If damaged Word document can no longer be opened even after the first emergency measures, you will get the specialized help in the preceding article. Following six tools are promising to rescue the contents, including document formatting, images, tables, footnotes and directories.
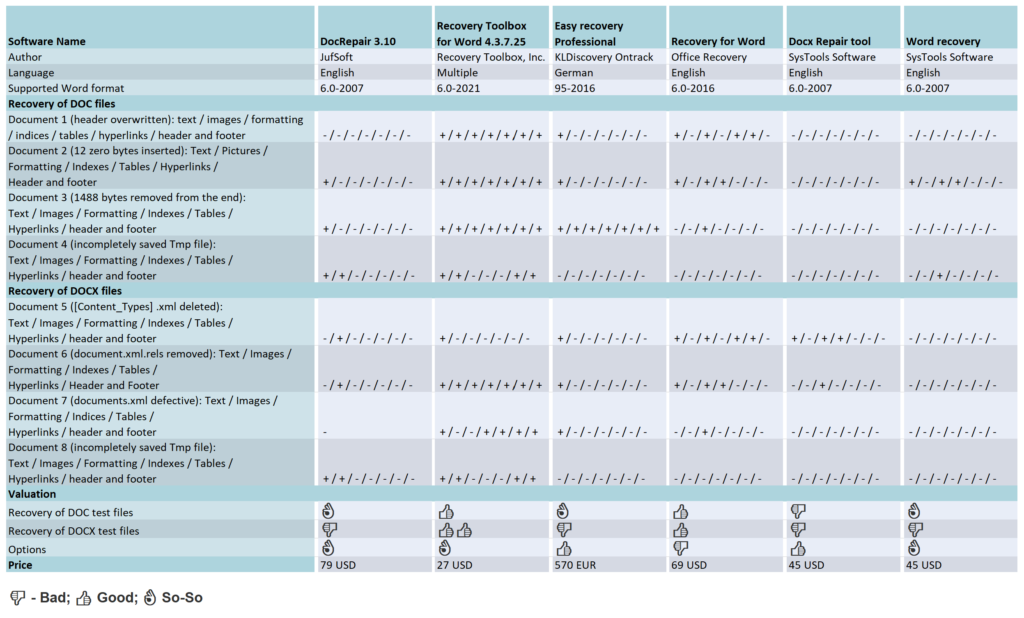
The complex binary structure of Word documents brings at a certain point own rescue attempts to fall. That’s why external tool providers are scenting the morning air. Our test shows what their special programs are capable of, which put the recovery talents of the following programs to the put to the test: DocRepair from Jufsoft, Recovery Toolbox for Word from Recovery Toolbox, EasyRecovery Professional from Kroll Ontrack, Recovery for Word from Recoveronix and the Systools products Docx Repair and Word Recovery. With the exception of Easy Recovery Professional, all programs programs require that the documents to be repaired are available as file and must exist. If you have deleted a Word file by mistake or formatted the memory card a classic data recovery program can track down lost data on the hard disk or other media and recover it, often even if the file system is no longer intact. This category also includes the program EasyRecovery which also belongs to this category, but with additional functions to also repair Word and other MS Office files.
All tools support the XML file format of Word 2007 with the extension DOCX for macro-free and DOCM for macro-containing documents. With the exception of Docx Repair all tested programs also understand the binary DOC format of earlier Word versions. With prices between 27 US Dollar and 570 Euro they are not exactly cheap. On the manufacturer’s pages test versions, which usually only cover the first page of a document, but at least show whether they can heal the specific document at all.
In order to examine the capabilities of the five of the five tools, we have three more complex documents of the same content in DOC and DOCX format with typical, but differently defects of varying severity. The manipulations performed with a hex editor manipulations on the DOC files looked as follows:
- Test document 1: Overwriting the header that identifies the file as a Word document (less serious)
- Test document 2: Insertion of 12 null bytes starting from byte position 54 (severe)
- Test document 3: Removal of 1488 bytes at the end of the file (severe)
Such defects occur in practice, for example, due to faulty file systems or unsuccessful removal of a macro virus, but also suddenly during work in Word. Unlike the binary DOC format, the (packed) document structure of DOCX files in the form of XML files is easy to recognize. Here, each file and each folder has a precisely defined function, which made the targeted reproduction of structural defects on three other test documents much easier:
- (see a note below)
- Test document 5: File [Content_Types].xml deleted, which virtually forms the table of contents of the XML structure (severe).
- Test document 6: File document.xml.rels removed. This contains references to embedded images, objects and so on (less serious).
- Test document 7: documents.xml file containing the actual document content, but mangled by removing some closing tags (severe).
Beyond file manipulation, we twice interrupted the saving process of a very long DOC and DOCX file to a USB stick by pulling it off prematurely. The temporary files left behind were test documents 4 and 8, which could not be opened by Word just as little as the other six.
The text program at least managed to almost completely restore test document 6 with the help of its own repair function – only the images were missing. The contents of the other documents could not be recovered completely, i.e. including the layout, even with the help of the own measures from the previous article.
The tested tools all have a simply structured English-language interface, on which there is not much to set or prepare. The user selects the damaged document, presses a button and after a certain waiting time, which the program needs for the analysis, receives a preview of the expected results. Mostly it is limited to the unformatted document text, a formatted display with images is afforded only by Docx Repair. In the rest of the cases, it is necessary to start the recovery and take a look at the newly created document to be able to judge the real extent of the recovery.
In all the programs tested, this process with an 18 MByte large Word document with around 800 pages took between 10 and 15 minutes. Even though none of the tested programs tampered with the original, it is recommended to always work with a copy of the document to rule out further damage, for example due to a power failure.
DocRepair
DocRepair has a clear interface designed as a wizard, which guides the user through the recovery process in four steps. Its course can be influenced in the second step by means of three checkboxes. By activating the first one, the user informs the program that the defective document is not an English document, which is probably not the case. Presumably – the help is limited to only six sentences is intended to serve the correct interpretation of umlauts. It is probably more important to check the second box, otherwise the tool will not attempt to recover images. The third checkbox puts DocRepair into “Salvage content retrieval mode”, which supposedly retrieves more content, but also more character garbage from the broken file.
However, switching on the “Afterburner” hardly improved these mediocre results. In the case of test document 1, DocRepair only brought to light character garbage, and in test documents 2 and 3, only unformatted text. In the case of test document 4, but scattered it over many “islands” in a sea of character garbage. Even poorer was the result with DOCX files. DocRepair was able to recover text and images from document 8, but for documents 5 and 6 it was only enough for the images. The analysis of test document 7 kept DocRepair so busy that the tool could only be freed from its rigidity by means of the Task Manager to free the tool from its rigidity.
Recovery Toolbox for Word
The interface of Recovery Toolbox for Word has the charm of a dialog box: it consists of a text field for specifying the damaged file and two buttons. When clicking on Analyze, the user is confronted with the superfluous question whether he really wants to start the process. :) After the analysis, the recovery result can be exported from the preview directly to Word in a newly created document or saved as plain text. The fact that Recovery Toolbox for Word offers a text file as an output option is no coincidence.
However direct output to Word brings all formatting to life. It succeeded in the case of test documents 1 to 3. During the analysis of test document 4 the program took 15 minutes to complete but the program was able to recover the text completely. With DOCX files (test documents 5 to 8), Recovery Toolbox was able to repair everything and returned completed document in all cases. All other formatting, images, functional text elements were also recovered.
EasyRecovery Professional
Apart from a few non-localized function names, EasyRecovery Professional is the only program in the test with has a German-language user interface. In contrast to the other tools, the 570 Euro program not only masters the repair of defective Word and other Office documents, it can also be used to analyze and fix hard disk problems, recover deleted files, and rescue damaged ZIP archives and e-mail data files from Outlook and Outlook Express. A graphical tab on the left side of the program window allows the user to switch between the different functional areas. The operation of the Word document repair function (Word Repair) is limited to three simple steps: select the damaged Word file, specify the destination folder for the recovered document and click “Next”.
The EasyRecovery does the rest on its own. It informs you about the progress in a status window and finally opens the recovered document in Word. In the destination folder, you will always find an additional document with the file name “_SAL” for Salvation. In this document EasyRecovery stores only the plain text, as far as it could recover it from the defective document. EasyRecovery was able to completely recover test document 3, including text, all images, formatting, indexes, tables, hyperlinks, and header and footer contents.
From the other DOC files, the program was only able to recover the text of the first paragraph. In the case of DOCX files, the tool also limited itself to the pure document text, but recovered it completely. EasyRecovery could not do anything with the incompletely saved test documents 4 and 8. Although the tool could be persuaded to open the the TMP files and reported on the performed recovery actions in a status window. However, the two resulting documents were empty.
Recovery for Word
Three graphical buttons adorn the interface of Recovery for Word. Clicking on Recover brings up a file dialog, which on our test computers only offered the mysterious file type “Web site is located on %s”. Word documents could only be selected by entering “*.*”. During the repair work, only a percentage bar and a less informative text display inform about the progress of the repair work, at the end of which there is only a short final report and a link to open the generated document. Recovery for Word achieved acceptable results when recovering test documents 1 to 3. In all cases, the text was preserved as completely as all pages and paragraph formatting, the table of contents, the keyword index and the table.
There were significant deviations from the original in character formatting (font and colors). The hyperlinks basically worked, but all pointed to the same jump target in the document. A footer mistakenly reappeared as a header, displacing its original content. The images, however, were all missing. When analyzing and repairing the defective DOCX files (test documents 5 to 7), Recovery for Word also achieved acceptable repair performance.
With the exception of umlauts, the text was complete in all cases, including character and paragraph formatting, footnotes, headers and footers, table, table of contents and index. The page layout did not match the original. Hyperlinks were only partially preserved, and only in test document 5. The program could not recover images in any case.
The program coped much worse with incomplete temporary files (test documents 4 and 8) than with DOC and DOCX files. We stopped the test after 60 minutes, during which the progress bar had not moved a millimeter.
SysTools Docx Repair
The interface of SysTools Docx Repair makes a tidy impression. The user clicks on the Browse button and selects the defective file. The file dialog only offers a filter for DOCX files, but entering “*.tmp” in the file field also makes temporary files selectable, which the program processes without any problems. A click on “Recover” brings up a small window that shows the progress of the analysis and repair work and wants to be confirmed with the OK button. After examining the preview, which always includes only the first document page, the user can specify via radio button whether he wants to save the result in a new DOCX document or as an RTF file. In the test, SysTools Docx Repair predominantly achieved very good results. For example, in the case of test document 5, the program managed a complete recovery, which included the entire text, all formatting, images and functional text elements. The generated DOCX file did not differ in any respect from the underlying original.
Document 8 was missing only the headers and footers, while Document 6 was missing the images. Finally, test document 7 certified severe damage, and program stopped without any feedback. A small flaw: Word 2007 initially refused to open the DOCX files created by Docx Repair in all cases. The automatically activated repair function of the text program was able to restore the allegedly unreadable documents back into shape but all other formatting, images, functional text elements – fell by the wayside.
SysTools Word Recovery
At first glance, you might confuse SysTools Word Recovery with DocRepair: The icons and also the wizard-like interfaces are almost identical. Differences only become apparent in “Step 2” of the recovery process, where you have to decide whether you want to recover all content and formatting (Quick Recovery), only images (Image Recovery) or only the bare essentials from particularly badly damaged Word documents (Salvage Recovery).
The full-bodied promise, however, the program could not come close to fulfilling the full promise of being able to recover text, images, diagrams including formatting. For example, it only recovered text from the first test document, but without umlauts and other special characters and here were missing two of four chapters.. In documents 2 and 3, the text was complete, but all formatting fell by the wayside, as did the images, which even the Image Recovery mode could not bring to light. When accessing the TMP files (test documents 4 and 8), the tool crashed in all modes. In the case of DOCX files 5 to 7, SysTools Word Recovery always hung up without leaving a usable result. It is hard to understand why the image recovery mode is not available for DOCX files of all things, especially since it would require only a small amount of programming.
Conclusion
If all attempts at manual repair have failed, there are really only two of the tested tools that can be considered for computer-assisted rescue attempts on Word documents:
Recovery Toolbox for Word and DocRepair. Both strive for a holistic recovery that includes all content and formatting if possible, while SysTools Docx Repair, Recovery for Word and EasyRecovery do much less and are mostly content with the plain text, which the user has to restore to its original form with a lot of effort. Recovery Toolbox for Word combines very good operation with the best overall recovery performance. DocRepair can only be used for defective documents in the Open XML format. Those who want to repair a defective DOC file will reach for Recovery Toolbox for Word, which still shows acceptable performance even for OpenXML documents.